Getting started with User Interface(UI)/User Experience(UX) Design
UI/UX designers role come in different forms depending on the shoes the designer is trying to fill in an enterprise or the project being worked on. A UI/UX designers duty cuts from the UI bit which involves the creation of aesthetically pleasing screens to the problem solving bits of UX that involves the end users. In this post, we would be looking at the basics you need to know in getting started with a career path in UI/UX.
Roles of UI/UX designers
UI roles entails all the aesthetic bits in a digital product that is in interaction with an end user. UI designers handle the designs we interact with on screen and operate mainly on the looks which might include design characteristics such a colour, spacing, typography and uniformity of design. They also specialize in interpreting brand values and strength through their designs.
UX roles involve the ideation and problem solving bits of a design. UX designers handle ideation, creation and testing of features and solutions in design. A UX designer thinks about how users feel , interacts and perceives a digital product. UX designers think about how well users interact with a product, their key goal is to improve the experience of the user. Roles of a UX designer goes beyond launch as they perform continuous testing of usability metrics and identify areas of improvements
Getting started with UI/UX
Getting started with UI/UX can be a challenging task for some newbies, it requires learning and researching the basics of UI/UX design , figuring out strength and skills, practice design and work on projects. Below, I will highlight some concept a designer needs to look into in order to aid their transition into the career path of UI/UX design.
- Design Tools: There are various design tools used by designers out there which serves specific purposes to designers depending on the task they strive to achieve or sometimes based on the tools used by companies they work with. Some of the very basic tools include;
 a. Figma
b. Sketch
c. Adobe XD
d. MiroBoard
e. Figjam.
a. Figma
b. Sketch
c. Adobe XD
d. MiroBoard
e. Figjam.
As an aspiring Designer, It is advisable to specialize in at least one of each UI and UX based tool as this helps improve learning pace
- UI Methodologies: In order to provide aesthetically pleasing designs that meet usability demands of a product, there are various UI learning topics to be understood to enable you create better designs. These include:
a. Colour b. Typography c. Iconography d. Layout and Spacing e. Responsive UI f. UI Trends g. Wireframing and Prototyping
- UX Methodologies: UX methods are ways of generating insights about your users, their behavior, motivations, and needs. You can use various user research methods to identify challenges and opportunities to improve on. The various methodologies involved in User Experience design include;
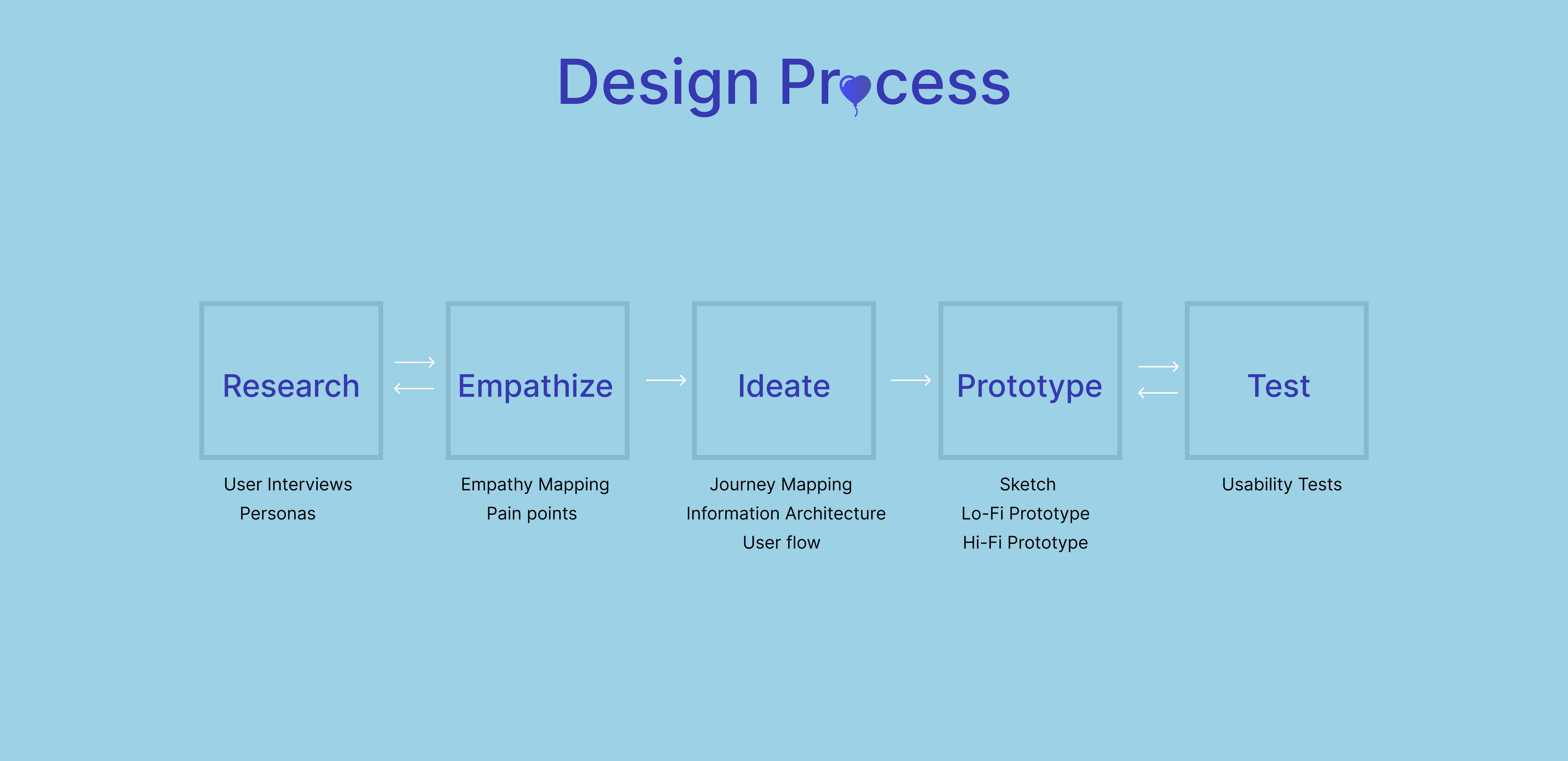 a. User Research
b. Empathy Mapping
c. Ideation
d. Journey Mapping/ User flow
e. Usability Testing
a. User Research
b. Empathy Mapping
c. Ideation
d. Journey Mapping/ User flow
e. Usability Testing
- Design Resources: All resources that aid in inspiring, presenting and faster deployment of design fall under design resources. These include contents such as books, inspiration tools, third party helper resources such as presentation tools , libraries and plugin tools.
 They help decrease the need to "Reinvent the wheel " in most design system processes.
They help decrease the need to "Reinvent the wheel " in most design system processes.
- Portfolio : Design portfolios enable designers showcase their designs and also enable them interact with fellow designers along with design trends.
 There are Third party platforms that enable designers develop, share and connect with designers. Examples of such platforms include: Behance, Dribble, Adobe portfolio, Corofloat
Cargo and Pixpa. Having an active portfolio helps in keeping up with UI trends and also serves as a source of design inspiration.
There are Third party platforms that enable designers develop, share and connect with designers. Examples of such platforms include: Behance, Dribble, Adobe portfolio, Corofloat
Cargo and Pixpa. Having an active portfolio helps in keeping up with UI trends and also serves as a source of design inspiration.
Every career path comes with its demand and commitment challenges which determines rate of improvement in it. Some soft skills needed by designers include
- Communication skills
- Collaboration
- Critical Thinking
- Teamwork
Designers can also build and improve their network, follow design experts along with their works for inspiration and active learning. Also, practice makes perfect so it is advised to practice your designs daily.

